Session Process
Each session follows a structured sequence to ensure reliable data. I anticipate that it will take a large number of sessions before I get a reliable brain response from the imagined body movements Below are the main steps in a session, from preparation to review.
1. Preparing the Cap
Before recording begins, the EEG cap is fitted with conductive gel at each electrode site. The gel helps the sensors make good contact with the scalp, reducing resistance and improving signal quality. It can be messy for the subject themselves to apply the gel. Fortunately my wife is quite good at it. It is also somewhat easier for those of us not blessed with hair in the chosen electrode areas!
2. Impedance Check
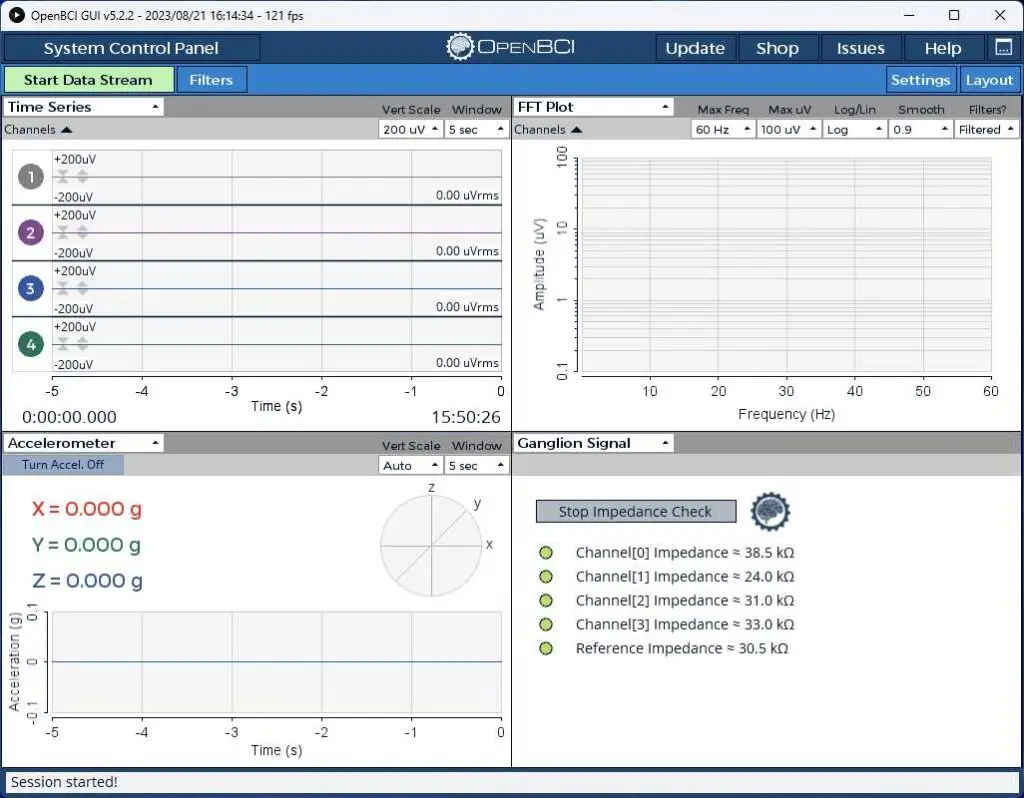
Once the cap is in place, we use the OpenBCI GUI to check electrode impedance. This is a free piece of software downloadable from the OpenBCI website. It does a lot more than check impedances! There are many configurable windows and features and of course it caters for a range of OpenBCI product such as Cyton and Cyton Daisy as well as the Ganglion. In this context, I am just using the Impedance Checking feature. You can see this in the lower right window of the illustration. The four channels represent the main electrode positions I have chosen. The EEG cap also connects a reference and a ground electrode to the Ganglion.
A healthy connection shows up as green on the screen (pale green, or even better, dark green).
If any channels are not green, adjustments are made to the cap and the gel until all electrodes are within the acceptable range. This step ensures that the data collected will be clean and reliable.
3. Calibration Run
Before the main imagery session, a short calibration run is performed. This records the participant’s baseline brain activity at rest. Calibration helps the system distinguish between background rhythms and the specific patterns generated during imagined movements.
4. Guided Session
With calibration complete, the participant begins the actual BCI session. The subject chooses the Motor Imagery button and starts the stream of data running from the Ganglion.
- On‑screen prompts and verbal guidance indicate what to imagine (for example, moving the left side or right side of the body).
- The on screen prompt changes every after short intervals, showing either Left, Right or Centre. Centre means no movement.
- The participant focuses on these mental tasks while the EEG system records the corresponding brain activity.
- Over time, the subject learns which type of imagery results in the most reliable response.
5. Reviewing the Logs
After the session, the recorded data is examined.
Logs show whether the system successfully detected the intended mental tasks.
Successes and misclassifications are noted, providing feedback for both the participant and the system.
These logs are essential for tracking progress across multiple sessions.
- These session logs are imported into Excel so that progress can be plotted and this is published on the Results So Far page.
Summary
The session process moves from preparation → verification → calibration → guided activity → review. Each step builds on the last, ensuring that the data is both accurate and meaningful for the project.
It is also important to remember to clean the EEG cap after a session. This avoids deterioration of the electrodes.
